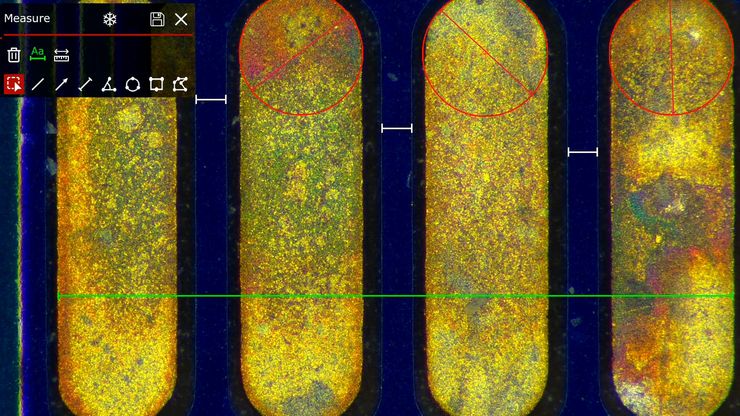
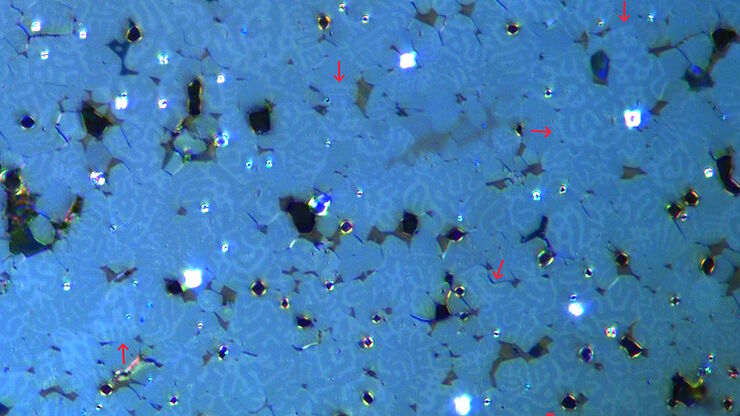
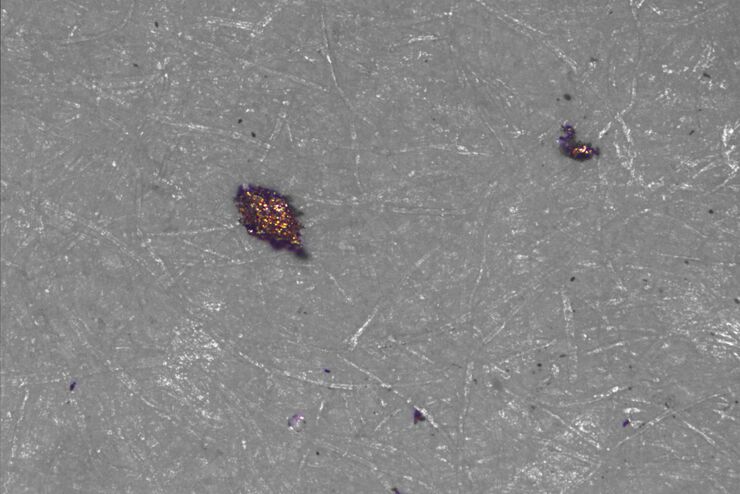
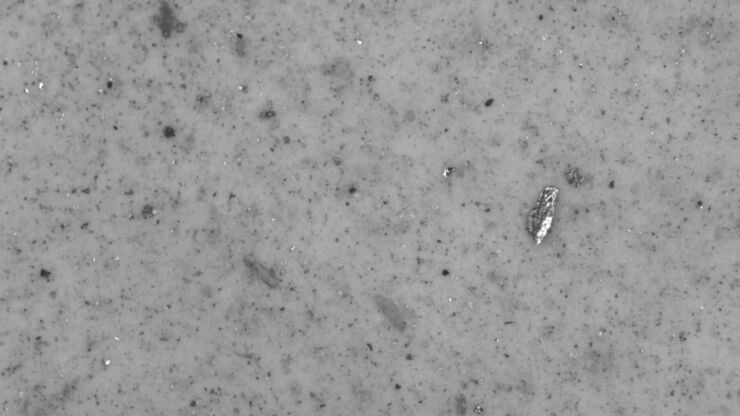
David R. Barbero , PhD

Dr. David R. Barbero ist Ingenieur und Physiker und verfügt über mehr als 15 Jahre Erfahrung mit optoelektronischen Materialien, Geräten und Displays im Nanobereich. Seine Arbeiten wurden in mehreren führenden Fachzeitschriften für Materialwissenschaft und Physik veröffentlicht und in über 300 wissenschaftlichen Zeitungen und Internet-Websites vorgestellt. Er verfügt über langjährige Erfahrung in der Nanomusterung und Nanostrukturierung von Polymeren und Verbundwerkstoffen (optische Lithografie, Nanoimprinting, kolloidale Nanoröhren und Polymerselbstorganisation). David promovierte in Physik am Cavendish Laboratory der Universität Cambridge (Vereinigtes Königreich), wo er als Marie-Curie-Stipendiat und European Cambridge Trust Scholar tätig war. 2009 wurde er mit dem Abdus-Salam-Zweitplatzierten-Preis der Universität Cambridge in Physik ausgezeichnet.