
Industrial Microscopy
Industrial Microscopy
Dive deep into detailed articles and webinars focusing on efficient inspection, optimized workflows, and ergonomic comfort in industrial and pathological contexts. Topics covered include quality control, materials analysis, microscopy in pathology, among many others. This is the place where you get valuable insights into using cutting-edge technologies for improving precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes as well as accurate pathological diagnosis and research.
Filter articles
Tags
Products
Loading...
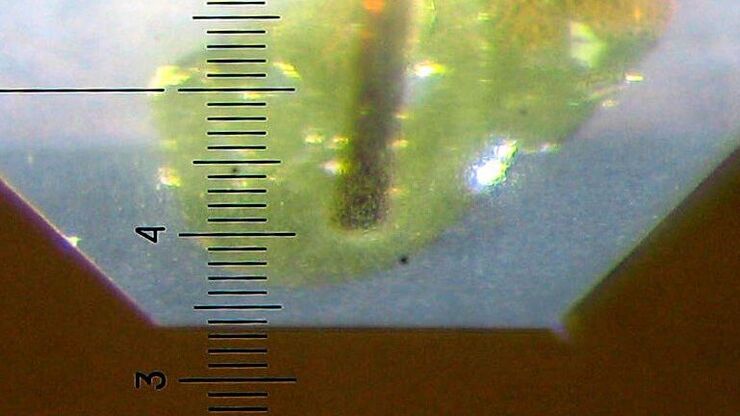

Brief Introduction to Specimen Trimming
Before ultrathin sectioning a sample with an ultramicrotome it has to be pre-prepared. For this pre-preparation, special attention must be paid to the sample size (size of the section), location of…
Loading...
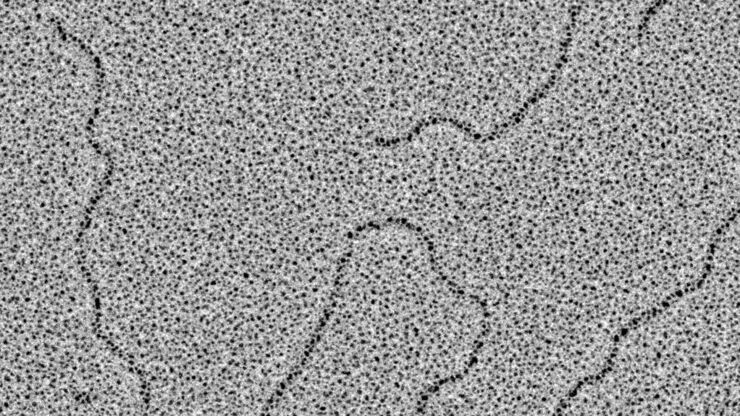
Glycerol Spraying/Platinum Low Angle Rotary Shadowing of DNA with the Leica EM ACE600 e-beam
Glycerol spraying/low angle rotary shadowing (Aebi and Baschong, 2006) is a preparation technique used in biology to visualize structures yielding insufficent contrast with other techniques, due to…
Loading...

Brief Introduction to Freeze Substitution
Freeze-substitution is a process of dehydration, performed at temperatures low enough to avoid the formation of ice crystals and to circumvent the damaging effects observed after ambient-temperature…
Loading...

Thermodynamic Considerations Regarding the LN2 in a High Pressure Freezer
Employing liquid nitrogen (LN2) as a coolant in the complex process of high pressure freezing raises certain considerations regarding phase transition not only of the liquid sample to be frozen but…
Loading...
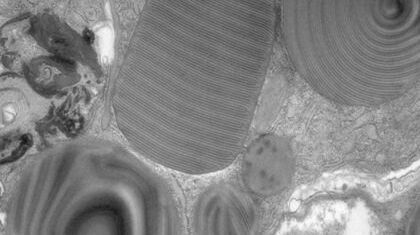
Brief Introduction to Contrasting for EM Sample Preparation
Since the contrast in the electron microscope depends primarily on the differences in the electron density of the organic molecules in the cell, the efficiency of a stain is determined by the atomic…
Loading...

Brief Introduction to Glass Knifemaking for Electron and Light Microscope Applications
Glass knives are used in an ultramicrotome to cut ultrathin slices of samples for electron and light microscope applications. For resin and for cryo sections (Tokuyasu samples) the knife edge must be…
Loading...

Brief Introduction to Coating Technology for Electron Microscopy
Coating of samples is required in the field of electron microscopy to enable or improve the imaging of samples. Creating a conductive layer of metal on the sample inhibits charging, reduces thermal…
Loading...
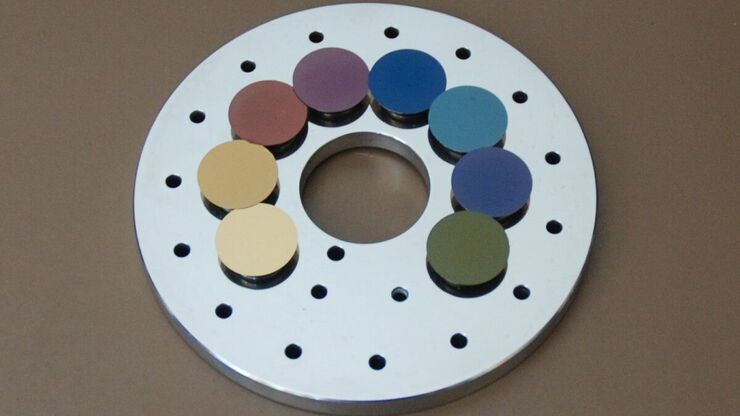

Carbon Thickness Evaluation in Electron Microscopy
The coating layers applied and used for electron microscopy imaging are commonly controlled and measured by quartz crystals. These crystals oscillate with a certain frequency (around 6 megahertz when…
Loading...
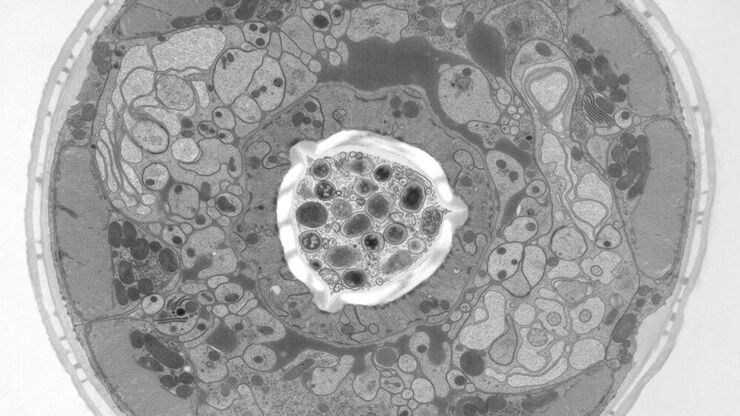
Brief Introduction to High-Pressure Freezing
Water is the most abundant cellular constituent and therefore important for preserving cellular ultra-structure. Currently the only way to fix cellular constituents without introducing significant…
