
Industrial Microscopy
Industrial Microscopy
Dive deep into detailed articles and webinars focusing on efficient inspection, optimized workflows, and ergonomic comfort in industrial and pathological contexts. Topics covered include quality control, materials analysis, microscopy in pathology, among many others. This is the place where you get valuable insights into using cutting-edge technologies for improving precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes as well as accurate pathological diagnosis and research.
Filter articles
Tags
Story Type
Products
Loading...
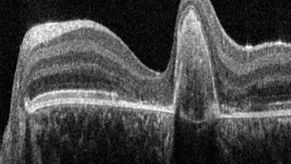
A Guide to OCT
Leica Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) systems support ophthalmologists, ophthalmic surgeons, and researchers with easy-to-use, high-quality imaging technology.
Loading...
A Guide to Zebrafish Research
For the best result during screening, sorting, manipulation, and imaging you need to see details and structures to make the right decisions for your next steps in research.
Known for outstanding…
Loading...
A Guide to Cryo-Electron Tomography
Cryo-electron tomography (CryoET) is used to resolve biomolecules within their cellular environment down to an unprecedented resolution below one nanometer.
Loading...

A Guide to Spatial Biology
What is spatial biology, and how can researchers leverage its tools to meet the growing demands of biological questions in the post-omics era? This article provides a brief overview of spatial biology…
Loading...

Technical Terms for Digital Microscope Cameras and Image Analysis
Learn more about the basic principles behind digital microscope camera technologies, how digital cameras work, and take advantage of a reference list of technical terms from this article.
Loading...

Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Stereo Microscope
This article explains key factors that help users determine which stereo microscope solution can best meet their needs, depending on the application.
Loading...
A Guide to Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM)
The fluorescence lifetime is a measure of how long a fluorophore remains on average in its excited state before returning to the ground state by emitting a fluorescence photon.
