What is cryo-electron tomography?
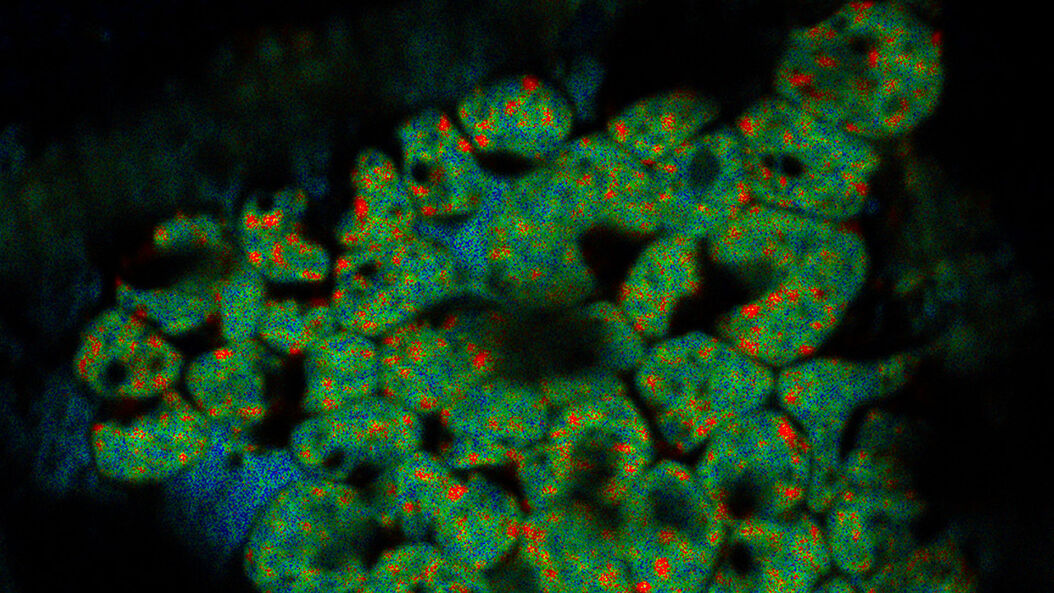
Cryo-electron tomography (also known as electron cryotomography) allows protein-protein interactions to be analyzed in three-dimensional molecular resolution in their native and functional state. The sample is imaged in a series of two-dimensional images as it is tilted in a controlled series of positions. The resulting image “slices” can then be combined to produce a 3D reconstruction of the sample.
Related articles
The Cryo-CLEM Journey
New Imaging Tools for Cryo-Light Microscopy
Improve Cryo Electron Tomography Workflow
What are the steps in a cryoET workflow?
The technique involves the preparation of samples, which are on electron microscopy grids and then rapidly plunge frozen into liquid nitrogen to vitrify the sample and prevent ice crystal formation.
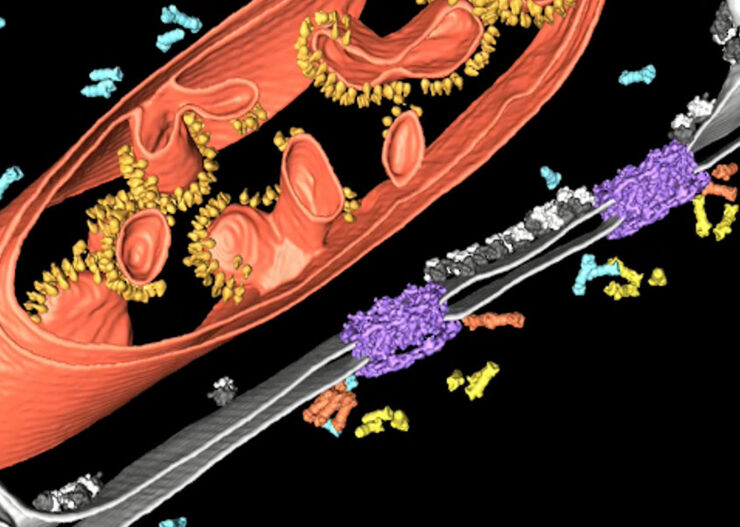
To perform high-resolution cryo tomography the imaged slice thickness of the specimen should not be bigger than 300 nm. For observation of “thicker” parts of the specimens, like cell bodies, the sample must be thinned. Beside cryo ultramicrotomy, Focused-Ion-Beam (FIB) Milling using a dedicated or multi-modal Cryo Scanning Electron Microscope is the method of choice. Two ion beam windows are positioned in such a way that a thin ice sheet (lamella) of about 200 nm thickness is created at the area of interest to make it accessible for Cryo ET.
The prepared samples can now be scanned with the cryo transmission electron microscope and afterwards, the data reconstruction process must take place to reconstruct the 2D images into a single 3D model.
What are the challenges in a typical cryoET workflow?
The biggest challenge associated with a typical CryoET workflow is related to the difficulty of identifying the precise area of interest containing the cell or protein to be imaged. Repeated failures in targeting can result in multiple repetitions of a time-consuming process, which ultimately wastes costly electron microscope (EM) imaging time. Two other challenges in the workflow include ensuring sample quality and ice thickness are consistent throughout, as well as keeping samples adequately vitrified before they are transferred to the cryo TEM.
How can cryoET challenges be overcome with cryo light microscopy?
Cryo light microscopy can positively contribute to the CryoET workflow in two important ways.
Firstly, light microscopy helps to assess the quality of the sample. The cryo light microscope gives a quick overview of the freezing quality and ice thickness of the sample as well as whether the sample distribution is optimal for further processing. Leica’s cryo solutions ensure that samples are kept safe and viable during these steps.
Secondly, the cryo light microscope’s greatest potential for greater workflow efficiency is the ability to target the structure of interest much more precisely before the time and cost intensive CryoEM preparations begin. Leica’s cryo light microscopy solutions enable image and coordinate export of the targeted structure towards subsequent EM steps, thereby greatly reducing EM imaging time.
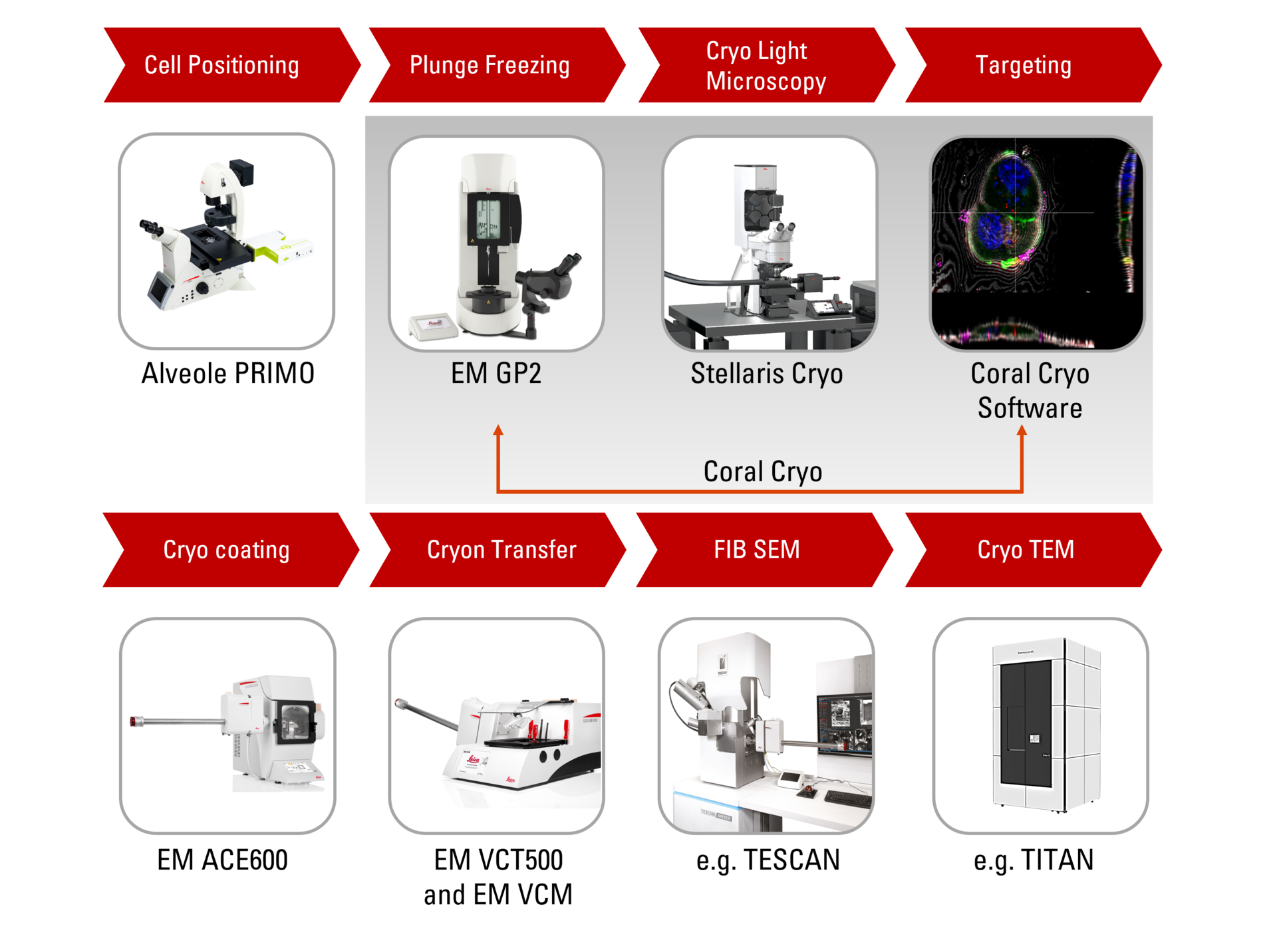
Introducing coral cryo: The effective cryoET workflow
Leica's dedicated 3D cryo-electron tomography workflow solutions overcome typical challenges by ensuring sample viability, quality checks and most of all, a precise and reliable 3D targeting mechanism. Make use of our optimized hardware, including cryostage and shuttle, in conjunction with state-of-the-art CryoET targeting software, as well as a variety of seamless integration and transfer options to cryo FIB or VCT stages.
Unlock precise 3D volume targeting
Find out how the seamless Cryo-Electron Tomography workflow Coral Cryo by Leica Microsystems uses confocal super resolution to target your structure of interest more precisely. The workflow reduces and optimizes the number of workflow steps, improves the sample loading and transfer and so enhances the productivity of the CryoET workflow.
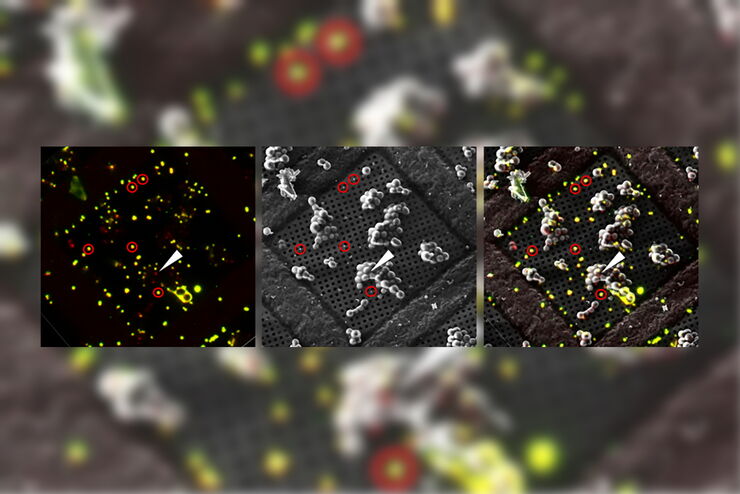
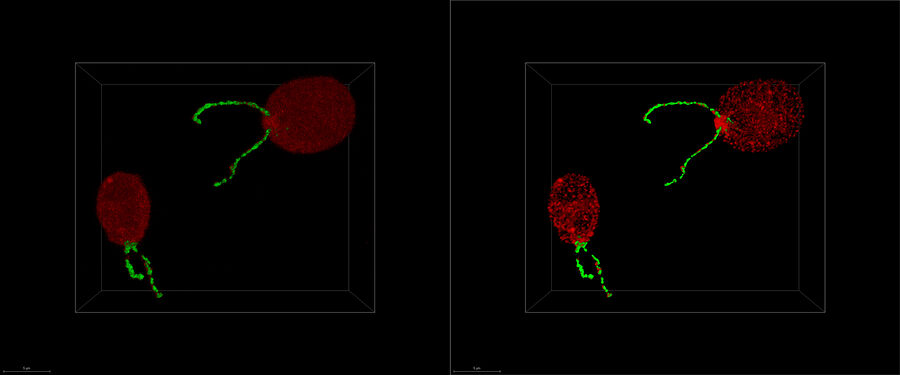
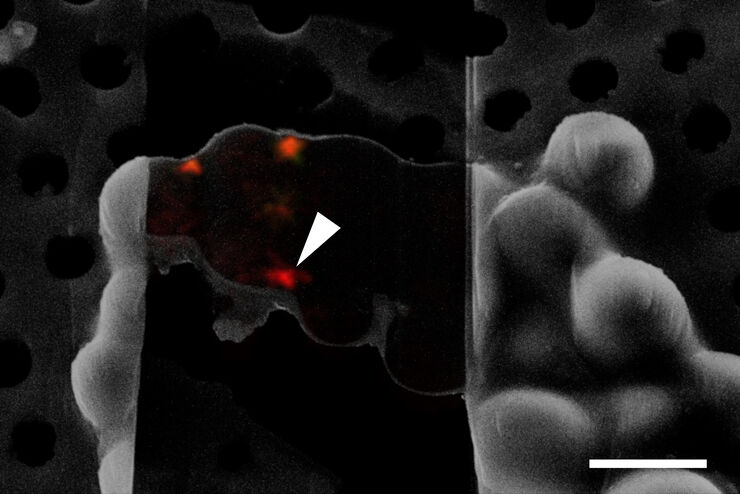
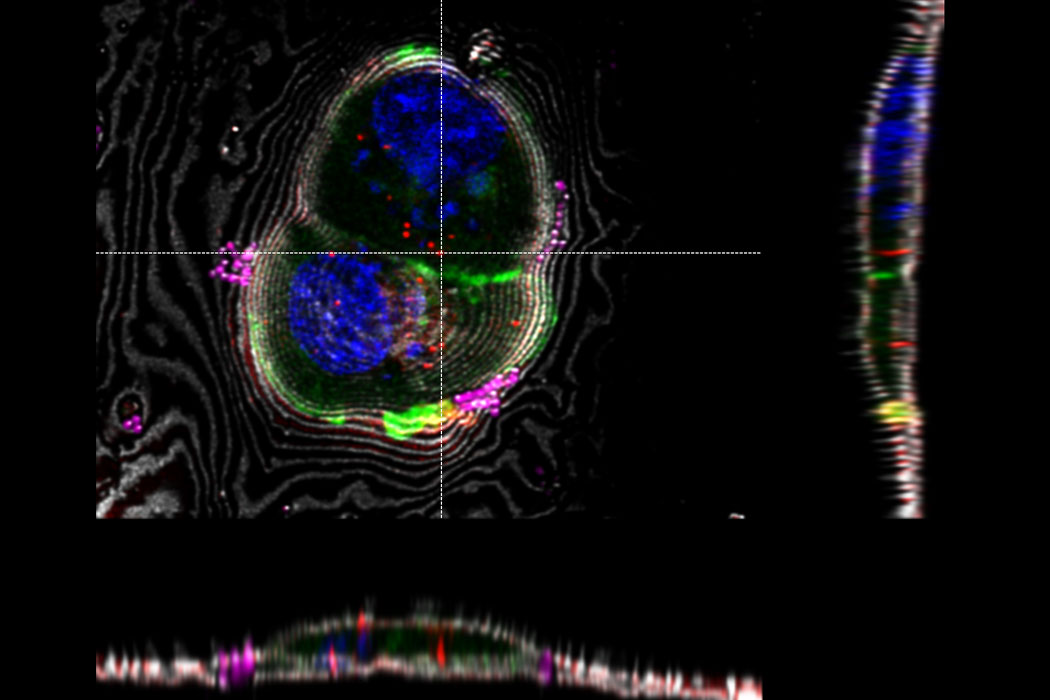
Overlay of a superresolved 3D confocal image with top SEM view (left panel) and FIB view (right panel). Overlay was performed using the beads as landmarks for the correlation. HeLa cells labeled as follows: nuclei by Hoechst, blue; mitochondria by MitoTracker Green, green; lipid Droplets by Bodipy and Crimson Beads, red). Scale bar: 20 μm. Cells kindly provided by Ievgeniia Zagoriy and SEM/FIB images kindly provided by Herman Fung, Mahamid-Group, EMBL-Heidelberg, Germany.
Related articles
How to Target Fluorescent Structures in 3D for Cryo-FIB Milling
Targeting Active Recycling Nuclear Pore Complexes using Cryo Confocal Microscopy
Advancing Cell Biology with Cryo-Correlative Microscopy
Workflows and Instrumentation for Cryo-electron Microscopy
What to Choose: Cryo Widefield or Cryo Confocal?
| Feature | Confocal | THUNDER (Widefield) |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | * | |
| Speed | * | |
| Lateral resolution | ** | * |
| Axial resolution | ** | * |
| Optimization of excitation and emission of dyes for cryogenic imaging conditions | ** | * |
| Suppression of Autofluorescence (Sample or Carbon layer) | * | |
| Targeting and export | 3D | 2D |