Learn about the transformative potential of multiplexed immunodetection
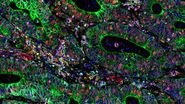
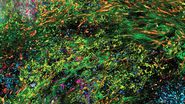
This application note underscores the transformative potential of multiplexed immunodetection in identifying and characterizing cancer stem cell niches within hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By simultaneously detecting a diverse array of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and tissue landmarks, this innovative approach reveals the intricate molecular composition of fibrous nests. These specialized tumor microenvironments have significant implications for the understanding of disease progression and overcoming treatment resistance.
Multiplexed imaging plays a crucial role in advancing cancer research by allowing scientists to delve deep into the complex microenvironments of tumors, unveiling unique characteristics and dynamic behaviors. This revolutionary technique concurrently visualizes various cell populations and their interactions within the tumor microenvironment, providing profound insights into the intricate ecosystem of tumors. This is indispensable for interpreting the tumor's reaction to therapeutic interventions, predicting treatment outcomes, and pinpointing potential targets for immunotherapeutic strategies. Multiplexed imaging is a vital tool aiding the ongoing quest to uncover cancer stem cell niches in hepatocellular carcinoma.
The integration of proteomics and multiplexed imaging empowers researchers to uncover the intricate nuances of cancer stem cell niches in hepatocellular carcinoma. The capabilities of Cell DIVE technology, coupled with the ClickWell slide carrier, are shown to streamline the process of multiplex immunostaining and reveal insights into intratumoral structures, fibrous nests and ECM. With comprehensive antibody validation and an iterative staining approach facilitated by Cell DIVE, researchers can simultaneously detect numerous proteins, enabling a deeper understanding of the tumor microenvironment.