Neuroscience Images taken with Mica
See how Mica can help scientists to image the human brain in different imaging modes such as Widefield and Confocal.
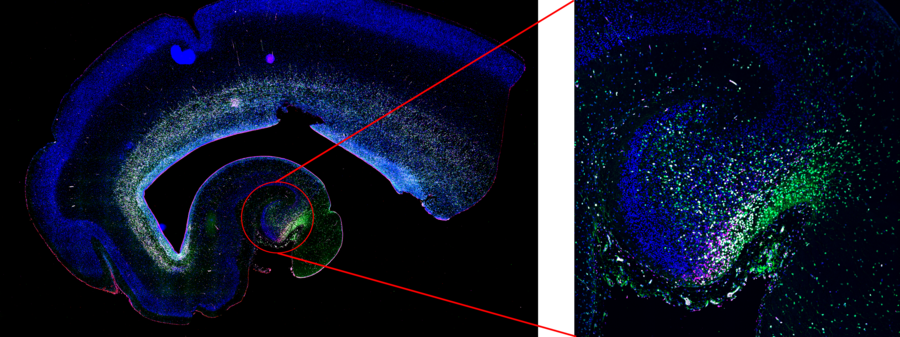
Mica - Human hippocampus
Piero Rigo at the Francis Crick Institute in London is interested in the development of the human brain from neural stem cells. As part of his work, he looks at the developing human neocortex at gestational week 18.
Gyrification is observed at the cortical plate, while proliferative neural progenitors, marked by Ki67, MCM2, and SOX2, populate the ventricular-subventricular zone. In the hippocampus, highly proliferative neural stem cells (green) are forming the dentate gyrus.
Neuroscience Images taken with THUNDER Imagers
See how THUNDER Imagers can help imaging cortical region of the human brain, Alzheimer’s plaques and D2 dopamine expression in mouse brain, neural spheroids and crest cells, cranial nerve development, axon regeneration, brain function after injury, disease, or aging.
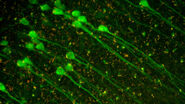
Mouse brain cortex
Virally labeled neuron

Mouse brain expressing of AMPK (red) in Microglia (IBA-1+, green)
Dr Ashok K. Shetty labat Texas A&M University (TAMU) is interested in developing clinically applicable strategies that are efficacious for enhancing brain function after injury, disease, or aging. One of the central areas is developing clinically feasible strategies for improving hippocampal neurogenesis and memory and mood function in aging and Alzheimer’s disease models via stimulation of endogenous neural stem/progenitor cells in neurogenic regions of the brain using drugs and biologics. Lab member Dr Maheedhar Kodali’s latest project is to check expression of AMPK in Microglia (IBA-1+) to know the effects of their investigating compound in aging.

Microglia in hippocampal region
Cortical neurons

Mouse Brain 1 mm Blood Vessels and nuclei CUBIC
Mouse embryonic kidney

Mouse cortical neuron

Adult rat brain

Uncleared human brain organoid
Neuroscience Images taken with STELLARIS confocal platform
Neuroscience studies require a variety of confocal imaging techniques to allow the study of the nervous system. For example, Multiphoton and light sheet techniques allow the study of large and deep tissues, such as brain sections; STED super-resolution is key to address neuronal spines structure, synaptic plasticity, and protein interactions at the synapse level. Fluorescence lifetime imaging can report on microenvironment changes in calcium and pH.
Gentle 3D live imaging of Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus
4 colour live imaging of mouse brain cortex
Neurodegenerative diseases are usually caused by a combination of different factors. Being able to visualize multiple players at once greatly helps to investigate and understand how different compoonents interact and influence each other. To do this, a microscope that combines deep tissue penetration with spectral flexibility to enable multicolor imaging liek STELLARIS 8 DIVE is the best choice.

Multicolor Deep In Vivo Imaging to uncover the interplay of various players in neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are usually caused by a combination of different factors. Being able to visualize multiple players at once greatly helps to investigate and understand how different compoonents interact and influence each other. To do this, microscope that combines deep tissue penetration with spectral flexibility to enable multicolor imaging like STELLARIS 8 DIVE is the best choice.

Tile scan overview of an unstained paraffin section of an adult Drosophila brain
STELLARIS confocal platform

Detail view from a tile scan of an unstained paraffin section of an adult Drosophila brain
STELLARIS confocal platform