
Life Science Research
Life Science Research
This is the place to expand your knowledge, research capabilities, and practical applications of microscopy in various scientific fields. Learn how to achieve precise visualization, image interpretation, and research advancements. Find insightful information on advanced microscopy, imaging techniques, sample preparation, and image analysis. Topics covered include cell biology, neuroscience, and cancer research with a focus on cutting-edge applications and innovations.
Filter articles
Tags
Story Type
Products
Loading...

Tracking Single Cells Using Deep Learning
AI-based solutions continue to gain ground in the field of microscopy. From automated object classification to virtual staining, machine and deep learning technologies are powering scientific…
Loading...

Learning the Cellular Architecture from its Optical Properties
In the last 3 years, microscopists have started to use "AI based" solutions for a wide range of applications, including image acquisition optimization (smart microscopy), object classification, image…
Loading...
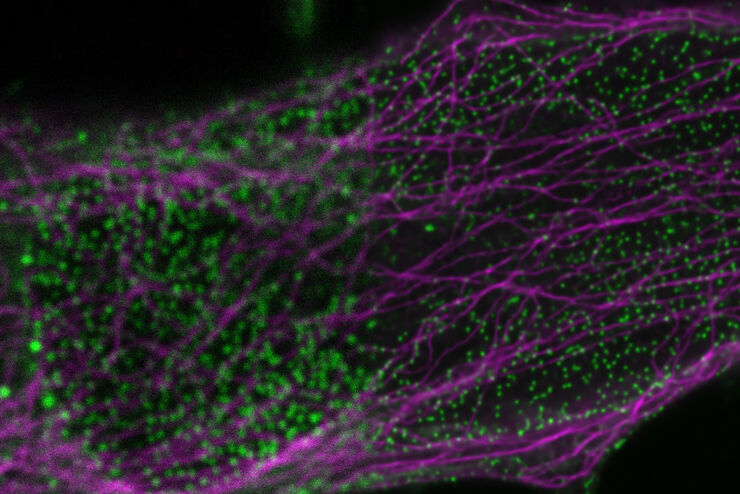
AI in Microscopy Webinar
We demonstrate residual channel attention networks for restoring and enhancing volumetric time-lapse (4D) fluorescence microscopy data.
