Key learnings
- Learn about the history of fluorescein sodium and ICG and their first applications in vascular neurosurgery
- Explore the advantages of fluorescence in neurosurgery and how it provides valuable information for neurosurgeons
- Watch videos of fluorescence-guided neurosurgery including arteriovenous malformations (AVM), bypass and aneurysm surgery clinical cases
Fluorescence in neurosurgery: History and first applications of fluorescein sodium & ICG
Fluorescein sodium has been used in neurosurgery since the late 1960s, and was first described by Fendel who performed epidural angiography during craniotomies. Indocyanine Green (ICG) was applied much later to assess cerebral blood flow. It was introduced at the beginning of the 2000s by Prof. Andreas Raabe, who decided to transpose this widely-used technique in ophthalmology to neurosurgery.
ICG was first used in neurosurgery to assess aneurysms, and was progressively applied to several neurosurgical pathologies: assessment of bypass permeability, AVM surgery, assessment of venous drainage anomalies in cavernoma surgery and neuro-oncology. Nowadays, cerebral fluorescent videoangiography is much more common with ICG.
Fluorescence-guided neurosurgery: Advantages & disadvantages of fluorescein sodium vs ICG
Fluorescein sodium videoangiography has some advantages compared to ICG videoangiography including a lower cost, the visualization of fine details and the ability to view directly in the microscope with a filter for fluorescence. ICG requires a separate infrared camera with the information displayed on a different screen. Fluorescein fluorescence also offers great value for retractorless surgery, which is very relevant as surgery becomes less invasive.
Another advantage of fluorescein sodium is that it is a relatively inert dye, with no special hazard for humans based on acute toxicity studies, although it can induce some serious allergic reactions. In addition, the cost is very low. A disadvantage of sodium fluorescein and one of the main differences with ICG is that it remains in the bloodstream for at least an hour requiring a long wait before it can be repeated.
ICG has a half-life of 3 to 4 minutes making it possible to perform a second or third injection within a short timeframe. However, it is contraindicated in certain patient populations such as patients with hypersensitivity to iodine or patients with hyperthyroidism. And it is much more expensive than fluorescein sodium, with a cost around 20 times higher.
Use of fluorescence for arteriovenous malformations (AVM) surgery
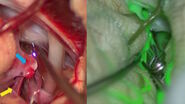
In a patient with left frontomesial AVM, a contralateral access was chosen, to avoid the dominant hemisphere and to have a better control on the feeder. The use of the Leica FL560 intraoperative fluorescein fluorescence module enabled precise visualization within the surgical field, through the microscope, of the timing, the feeder, the vein and the short vessels around the AVM with clear contrast.
With ICG however, the user has to look at another screen and it is not possible to see the surroundings of the AVM. Interpretation must be done by shifting from the monitor to the surgical field. Fluorescein fluorescence makes it easier to identify feeding vessels directly in the surgical field and offers better visualization of the parenchymogram.
Use of fluorescence for bypass surgery
In a patient with Moyamoya disease, a superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery (STA-MCA) bypass was performed. Fluorescein sodium fluorescence was very useful to explore and check the STA as well as see the functionality of the artery with direct vision in the surgical field. It is a very effective technique to understand how the bypass works. It offers good visualization of vessels and tissue perfusion, although thick vessels are less evident.
Use of fluorescence for aneurysm surgery
In a patient with a small aneurysm of the MCA, the use of fluorescein fluorescence supported the clipping. The contrast helped to expose the aneurysm and see the perforators and their perfusion in the surgical field directly. This can be missed with ICG, as it requires to look at another screen and the image is in black and white. With fluorescein fluorescence, an occluded aneurysm is clearly visible. However, it cannot be repeated as aneurysm surgery tends to be quite quick and thick vessels are also less evident. Fluorescein sodium can be used in combination with ICG, they are not mutually excluding.
As a conclusion, compared with ICG videoangiography, fluorescein videoangiography has the advantage of three-dimensional visualization in the surgical field and allows real-time surgical manipulation, especially of small vessels in a narrow field. In addition, it has a much lower cost. The disadvantages of fluorescein videoangiography are the incompetence in visualizing flow in thick-walled vessels and the longer period for which the dye remains in the blood. Both fluorescence techniques offer significant benefits for neurosurgeons.
Want to learn more? Register below to watch the full webinar presented by Prof. Marco Cenzato and see the clinical cases he shared.
The statements of the healthcare professional in this video reflect only his opinion and personal experience. His statements do not necessarily reflect the opinion of any institution with whom he is affiliated. Off-label uses of products are discussed in the presentation. Please check with your Leica Microsystems representative for the current regulatory indications in your region.