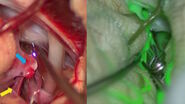
Augmented Reality & Mixed Reality in neurosurgery
Augmented Reality (AR) has significantly improved visualization in neurosurgery. It can enhance precision in relation to the patient compared to classical neuronavigation, by correlating with the patient head and anatomical features. Another valuable modality is fluorescence-guided neurosurgery and videoangiography. Overcoming the limitations of ICG, GLOW800 Augmented Reality provides surgeons with augmented information in the surgical field, allowing them to assess patient anatomy and the perfusion of blood vessels. GLOW800 AR combines white light image with real-time fluorescence imaging in a digitally-processed image superimposed on the blood vessels.
During aneurysm surgery, surgeons can verify in real time that all branches are open and perfused while the aneurysm is excluded from the circulation thanks to the green fluorescence in the blood vessels, can . There is no need to move away from the surgical field, optimizing the workflow.Fluorescence imaging as well as data from the IGS system help to further augment the surgeon's reality during surgery. The CaptiView image injection module from Leica Microsystems provides this information directly in the eyepieces.
However, fluorescence does not allow surgeons to see structures below the surface, even if it provides an initial check and helps identify early warning signs of a problem. As such, intraoperative angiograms remain a useful confirmation tool to ensure the correct exclusion and patency of all vessels.
Advantages of fluorescence-guided neurosurgery with GLOW800
A case series was recently published [1] looking at 40 cases using GLOW800: 33 cerebral aneurysms, 4 arteriovenous malformations and 3 extracranial-intracranial (EC-IC) bypasses for Moyamoya disease. The authors looked at vessel patency for aneurysms, flow characteristics for arteriovenous malformations and patency of EC-IC bypasses. The results show an excellent correlation of intra-operative angiography and ICG. The study also identified specific advantages of Augmented Reality fluorescence for different types of surgery.
Type of Surgery | Subjective Advantage | ||
Aneurism | Manipulation of the cerebral tissue to visualize small perforators | Time saving recognition of aneurysm remnant or occlusion of parent vessels | Repetitive use possible in case of clip replacement |
AVM | Quick identification of the feeding arteries and draining veins due to analysis of their flow dynamic | Visuatization of the cerebral cortex in combitation with the AVM vessels faciliates anatomical orientation and resection | Repetitive use possible for anatomical orientation |
Bypass | Patency of the superficial temporal artery after dissection and microanastomosis | Observation of capillary filling at the cortical surface pre- and post-completion of the anastomosis | Repetitive use possible for visualization pre- and post-bypass surgery |
Table 1: Subjective advantages of MFL AR compared to conventional methods (ICG-VA, microdoppler, DSA). Greuter L et al. World Neurosurgery 2021 accepted.
Use of Virtual Reality in neurosurgery
Virtual Reality plays an increasingly important role in surgical education, with immersiveness helping to expedite learning and increase its durability. A randomized trial comparing Virtual Reality to standard imaging in teaching has shown that, when using Virtual Reality, less experience is required to detect a particular situation.
In addition, Virtual Reality can be used for surgical planning with residents and directly integrated in the neurosurgical workflow. It offers a better understanding of the vascular anatomy prior to surgery. Virtual Reality also supports patient education and facilitates the discussion, for example through virtual craniotomies. This can increase patient trust
Towards heads-up display surgery
The goal is to integrate all the digital information in the operating room, which can be done through heads-up display surgery for example with the ARveo 8 Augmented Reality platform. It allows to combine the information provided by the microscope, Augmented Reality, neuronavigation and fluorescence.
The entire team can watch the surgery on 3D screens, including residents and visitors. The use of the exoscopic technique can also improve ergonomics in the operating room. With the Leica ARveo 8 microscope, there is a 600mm working distance which means the surgeon can have a normal standing position and better ergonomics through the use of the heads-up display, as there is less twisting or bending of the body during the procedure.
In the future, all surgical information could be available on head-mounted displays, reducing the footprint in the operating room. The surgical microscope could become a central hub to connect and seamlessly integrate all the data sources.
Want to learn more? Register below to watch the full webinar presented by Prof. Raphael Guzman and see the clinical cases he shared.
Note: The statements of the healthcare professional in this video reflect only his opinion and personal experience. His statements do not necessarily reflect the opinion of any institution with whom he is affiliated. Please check with your local Leica Microsystems representative for product registration status in your region.
Disclaimer: GLOW800 is not currently available in 3D