
Science Lab
Science Lab
The knowledge portal of Leica Microsystems offers scientific research and teaching material on the subjects of microscopy. The content is designed to support beginners, experienced practitioners and scientists alike in their everyday work and experiments. Explore interactive tutorials and application notes, discover the basics of microscopy as well as high-end technologies – become part of the Science Lab community and share your expertise!
Filter articles
Tags
Story Type
Products
Loading...
Handbook of Optical Filters for Fluorescence Microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy and other light-based applications require optical filters that have demanding spectral and physical characteristics. Often, these characteristics are application-specific and…
Loading...

Carbon Thickness Evaluation in Electron Microscopy
The coating layers applied and used for electron microscopy imaging are commonly controlled and measured by quartz crystals. These crystals oscillate with a certain frequency (around 6 megahertz when…
Loading...
Spectral Detection – How to Define the Spectral Bands that Collect Probe-specific Emission
To specifically collect emission from multiple probes, the light is first separated spatially and then passes through a device that defines a spectral band. Classically, this is a common glass-based…
Loading...
Brief Introduction to High-Pressure Freezing
Water is the most abundant cellular constituent and therefore important for preserving cellular ultra-structure. Currently the only way to fix cellular constituents without introducing significant…
Loading...

Step by Step Guide for FRAP Experiments
Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) has been considered the most widely applied method for observing translational diffusion processes of macromolecules. The resulting information can be…
Loading...
Every Clue Counts – Forensics Inconceivable Without Microscopy
There is no crime without clues. They may be obvious, like a cartridge case at the scene of the crime or clear signs of crowbar damage on a door. But sometimes, clues are microscopically small.…
Loading...
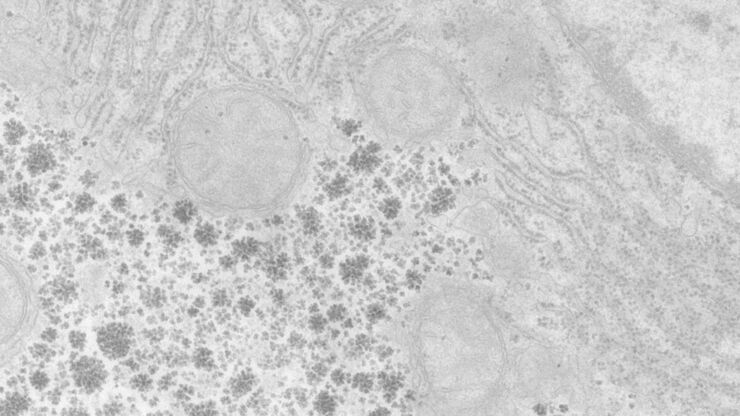
Perusing Alternatives for Automated Staining of TEM Thin Sections
Contrast in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is mainly produced by electron scattering at the specimen: Structures that strongly scatter electrons are referred to as electron dense and appear as…
Loading...

Widefield Calcium Imaging with Calcium Indicator Fura2
In eukaryotic cells Ca2+ is one of the most widespread second messengers used in signal transduction pathways. Intracellular levels of Ca2+ are usually kept low, as Ca2+ often forms insoluble…
Loading...
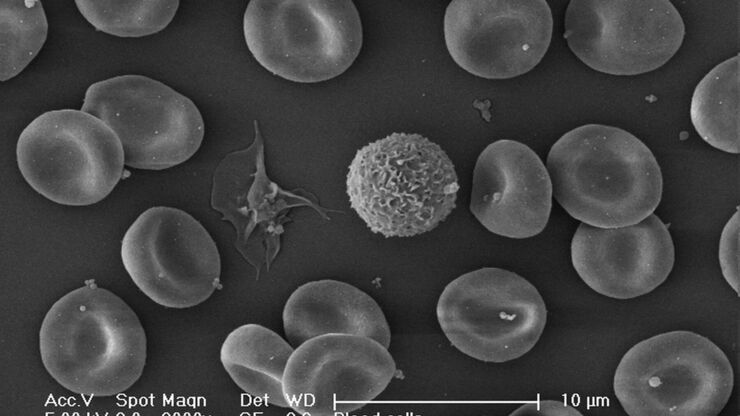
Brief Introduction to Critical Point Drying
One of the uses of the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) is in the study of surface morphology in biological applications which requires the preservation of the surface details of a specimen. Samples…
