
Science Lab
Science Lab
The knowledge portal of Leica Microsystems offers scientific research and teaching material on the subjects of microscopy. The content is designed to support beginners, experienced practitioners and scientists alike in their everyday work and experiments. Explore interactive tutorials and application notes, discover the basics of microscopy as well as high-end technologies – become part of the Science Lab community and share your expertise!
Filter articles
Tags
Story Type
Products
Loading...

How to Study Gene Regulatory Networks in Embryonic Development
Join Dr. Andrea Boni by attending this on-demand webinar to explore how light-sheet microscopy revolutionizes developmental biology. This advanced imaging technique allows for high-speed, volumetric…
Loading...
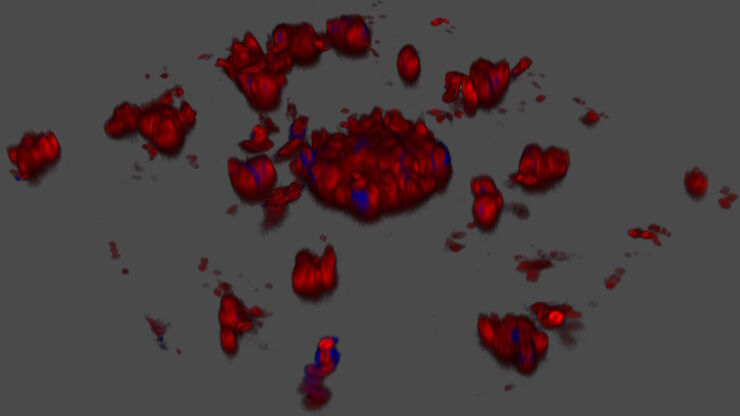
Exploring Microbial Worlds: Spatial Interactions in 3D Food Matrices
The Micalis Institute is a joint research unit in collaboration with INRAE, AgroParisTech, and Université Paris-Saclay. Its mission is to develop innovative research in the field of food microbiology…
Loading...
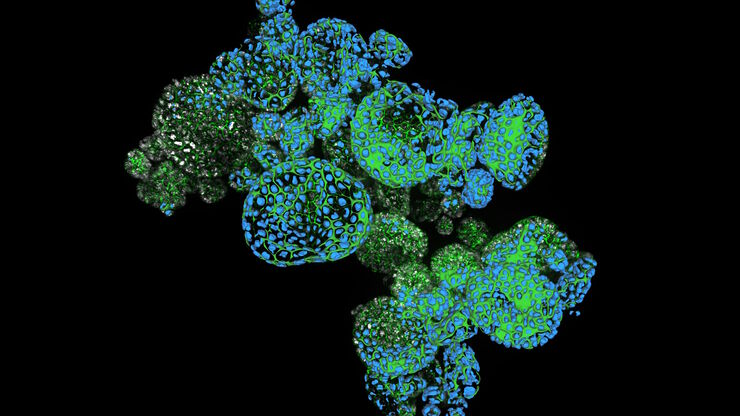
How Efficient is your 3D Organoid Imaging and Analysis Workflow?
Organoid models have transformed life science research but optimizing image analysis protocols remains a key challenge. This webinar explores a streamlined workflow for organoid research, starting…
Loading...

Overcoming Observational Challenges in Organoid 3D Cell Culture
Learn how to overcome challenges in observing organoid growth. Read this article and discover new solutions for real-time monitoring which do not disturb the 3D structure of the organoids over time.
Loading...

Notable AI-based Solutions for Phenotypic Drug Screening
Learn about notable optical microscope solutions for phenotypic drug screening using 3D-cell culture, both planning and execution, from this free, on-demand webinar.
Loading...

How to Get Deeper Insights into your Organoid and Spheroid Models
In this eBook, learn about key considerations for imaging 3D cultures, such as organoids and spheroids, and discover microscopy solutions to shed new insights into dynamic processes in 3D real-time
Loading...
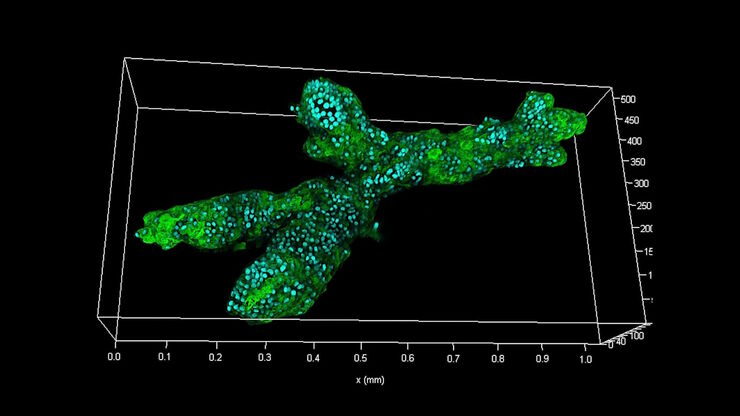
Examining Developmental Processes In Cancer Organoids
Interview: Prof. Bausch and Dr. Pastucha, Technical University of Munich, discuss using microscopy to study development of organoids, stem cells, and other relevant disease models for biomedical…
Loading...
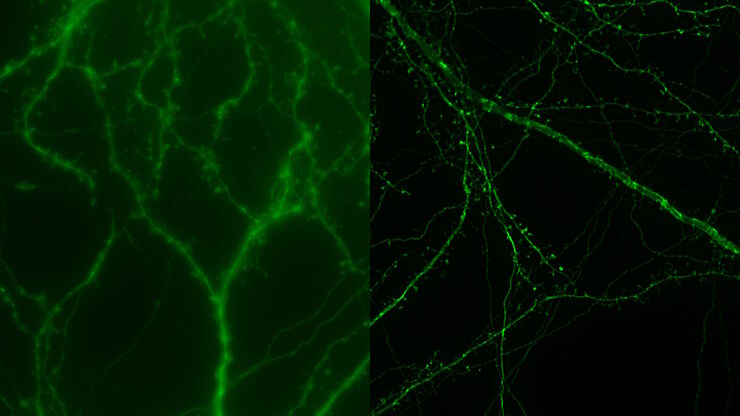
How Microscopy Helps the Study of Mechanoceptive and Synaptic Pathways
In this podcast, Dr Langenhan explains how microscopy helps his team to study mechanoceptive and synaptic pathways, their challenges, and how they overcome them.
Loading...

Unlocking Insights in Complex and Dense Neuron Images Guided by AI
The latest advancement in Aivia AI image analysis software provides improved soma detection, additional flexibility in neuron tracing, 3D relational measurement including Sholl analysis and more.
