
Science Lab
Science Lab
The knowledge portal of Leica Microsystems offers scientific research and teaching material on the subjects of microscopy. The content is designed to support beginners, experienced practitioners and scientists alike in their everyday work and experiments. Explore interactive tutorials and application notes, discover the basics of microscopy as well as high-end technologies – become part of the Science Lab community and share your expertise!
Filter articles
Tags
Story Type
Products
Loading...
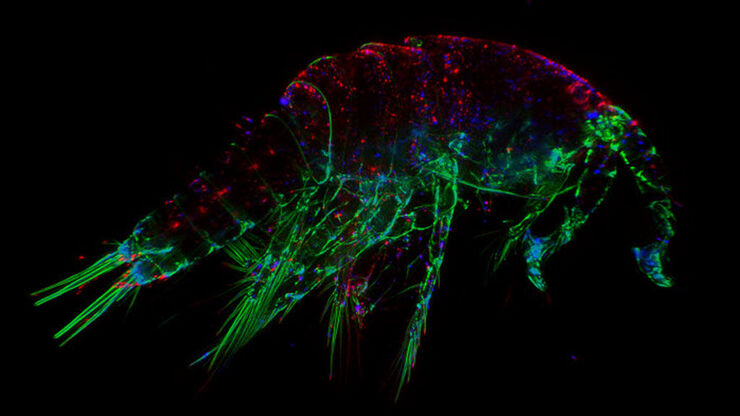
The Fundamentals and History of Fluorescence and Quantum Dots
At some point in your research and science career, you will no doubt come across fluorescence microscopy. This ubiquitous technique has transformed the way in which microscopists can image, tag and…
Loading...

Eyepieces, Objectives and Optical Aberrations
This article covers the components of the eyepieces and how to adjust them correctly to suit your eyes.
Loading...
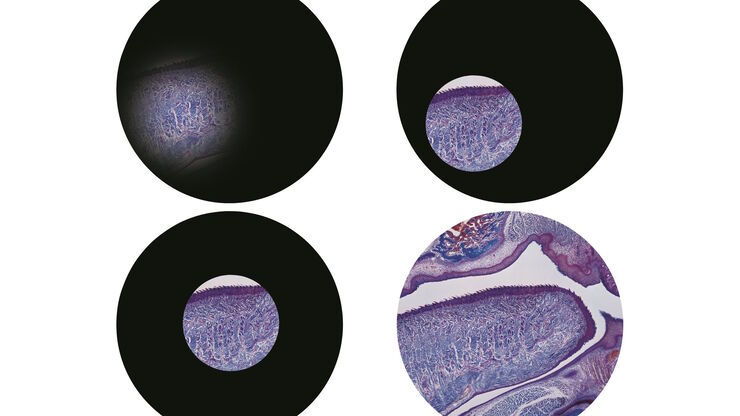
Koehler Illumination: A Brief History and a Practical Set Up in Five Easy Steps
In this article, we will look at the history of the technique of Koehler Illumination in addition to how to adjust the components in five easy steps.
Loading...
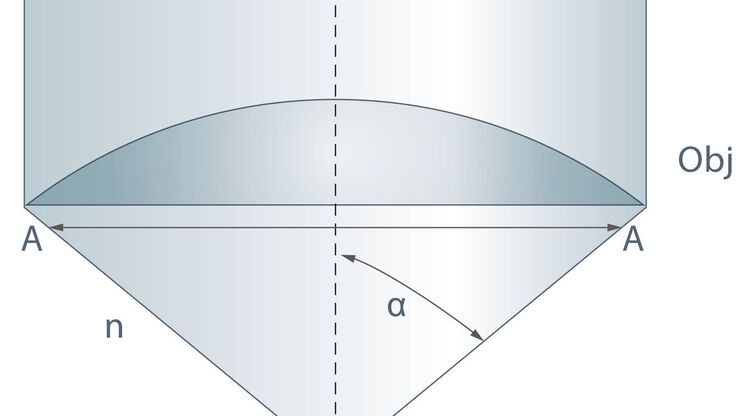
Collecting Light: The Importance of Numerical Aperture in Microscopy
Numerical aperture (abbreviated as ‘NA’) is an important consideration when trying to distinguish detail in a specimen viewed down the microscope. NA is a number without units and is related to the…
Loading...
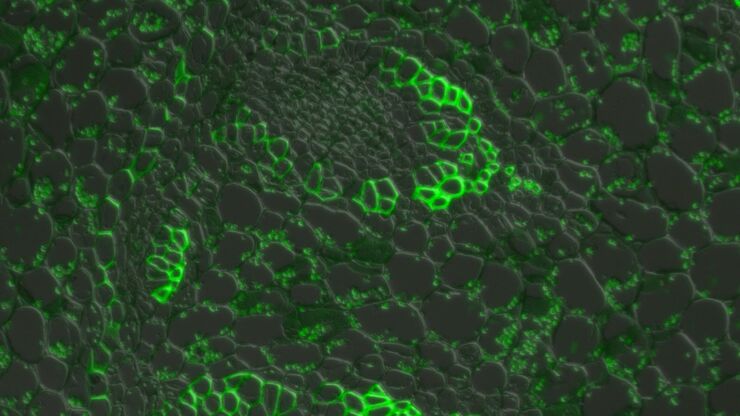
Introduction to Widefield Microscopy
This article gives an introduction to widefield microscopy, one of the most basic and commonly used microscopy techniques. It also shows the basic differences between widefield and confocal…
Loading...
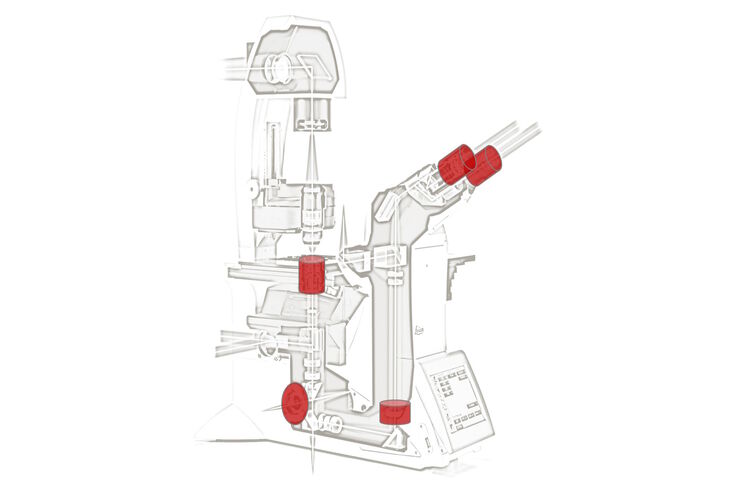
Optimization of the Interplay of Optical Components for Aberration Free Microscopy
Optical microscopes are used to magnify objects which are otherwise invisible for the human eye. For this purpose high quality optics is necessary to achieve appropriate resolution. However, besides…
Loading...

Milestones in Incident Light Fluorescence Microscopy
Since the middle of the last century, fluorescence microscopy developed into a bio scientific tool with one of the biggest impacts on our understanding of life. Watching cells and proteins with the…
Loading...
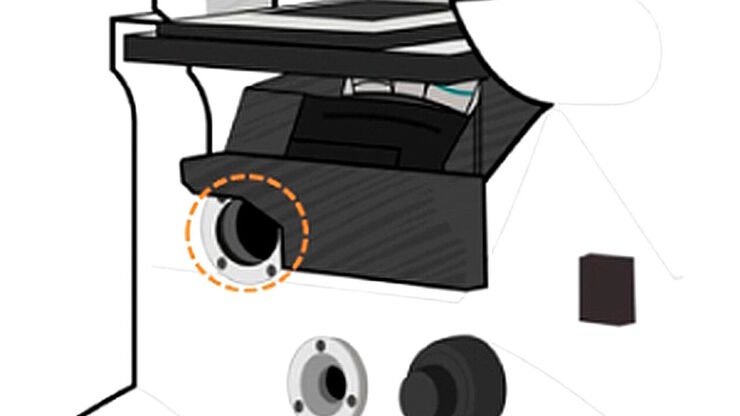
Infinity Optical Systems
“Infinity Optics” refers to the concept of a beam path with parallel rays between the objective and the tube lens of a microscope. Flat optical components can be brought into this “Infinity Space”…
Loading...
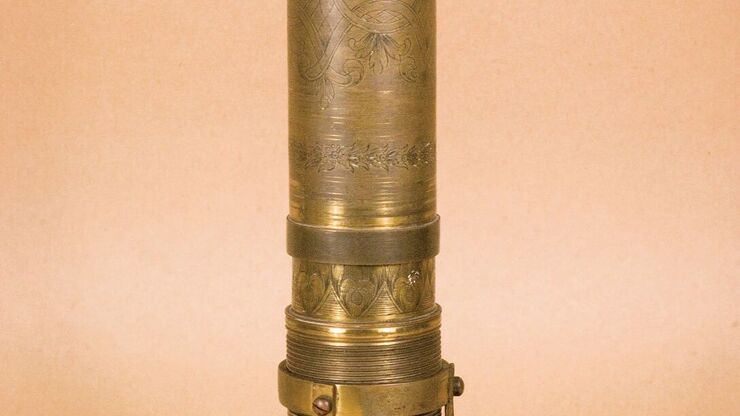

A Brief History of Light Microscopy
The history of microscopy begins in the Middle Ages. As far back as the 11th century, plano-convex lenses made of polished beryl were used in the Arab world as reading stones to magnify manuscripts.…
