Filter articles
标签
Story Type
Products
Loading...
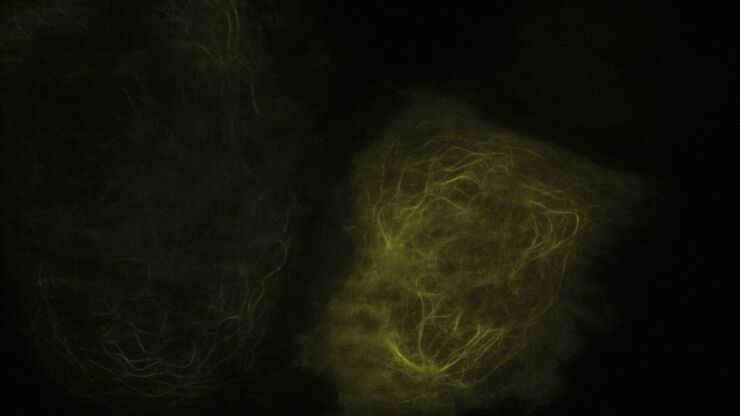
Applications of TIRF Microscopy in Life Science Research
The special feature of TIRF microscopy is the employment of an evanescent field for fluorophore excitation. Unlike standard widefield fluorescence illumination procedures with arc lamps, LEDs or…
Loading...
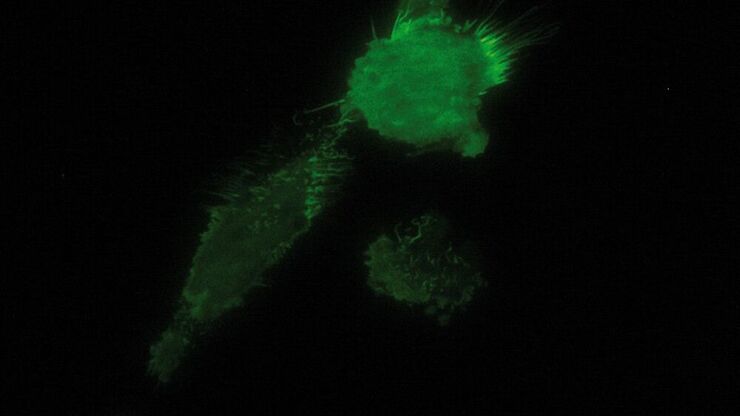
Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence (TIRF) Microscopy
Total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) is a special technique in fluorescence microscopy developed by Daniel Axelrod at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor in the early 1980s. TIRF microscopy…
Loading...
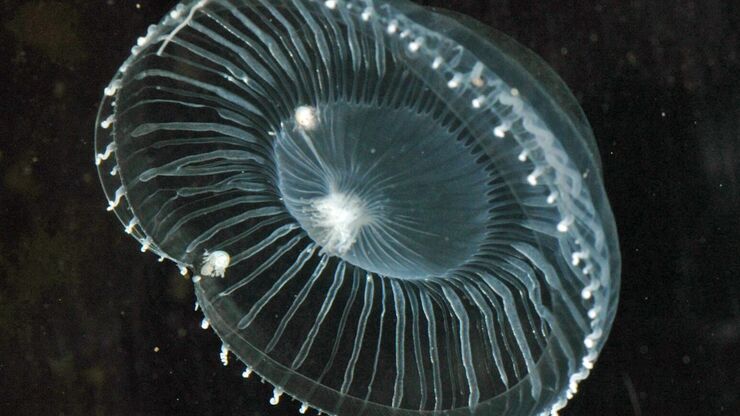

Fluorescent Proteins - From the Beginnings to the Nobel Prize
Fluorescent proteins are the fundament of recent fluorescence microscopy and its modern applications. Their discovery and consequent development was one of the most exciting innovations for life…
Loading...

Ratiometric Imaging
Many fundamental functions of a cell strongly depend on delicate, but nevertheless dynamic balances of ions (e.g. calcium, magnesium), voltage potentials and pH between the cell’s cytosol and the…
Loading...
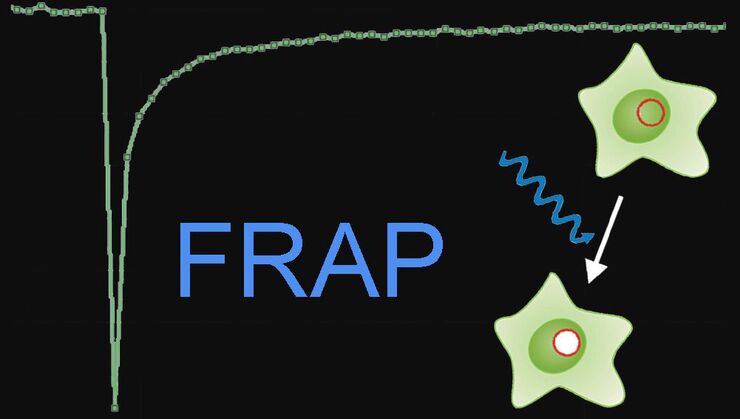
Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching (FRAP) and its Offspring
FRAP (Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching) can be used to study cellular protein dynamics: For visualization the protein of interest is fused to a fluorescent protein or a fluorescent dye. A…
Loading...

Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
The Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) phenomenon offers techniques that allow studies of interactions in dimensions below the optical resolution limit. FRET describes the transfer of the energy…
Loading...
An Introduction to CARS Microscopy
CARS overcomes the drawbacks of conventional staining methods by the intrinsic characteristics of the method. CARS does not require labeling because it is highly specific to molecular compounds which…
Loading...
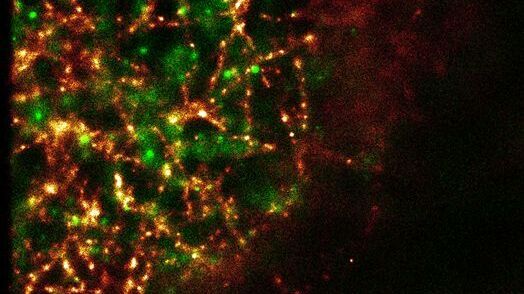
Super-Resolution GSDIM Microscopy
The nanoscopic technique GSDIM (ground state depletion microscopy followed by individual molecule return) provides a detailed image of the spatial arrangement of proteins and other biomolecules within…
Loading...
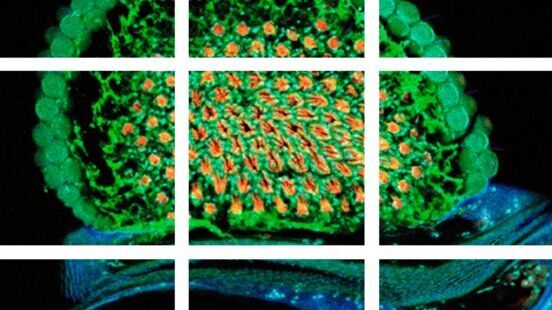
Mosaic Images
Confocal laser scanning microscopes are widely used to create highly resolved 3D images of cells, subcellular structures and even single molecules. Still, an increasing number of scientists are…

