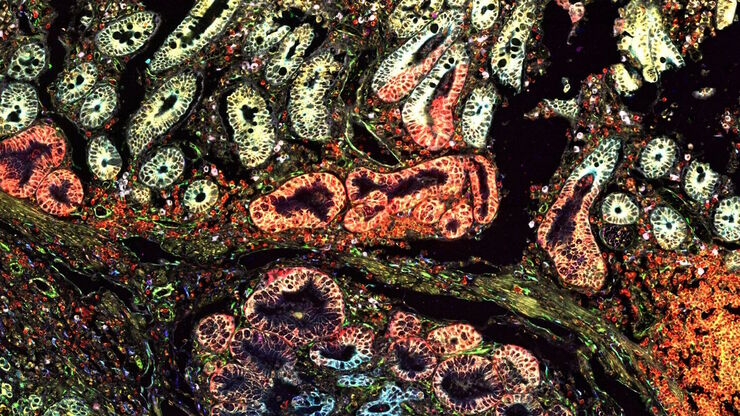
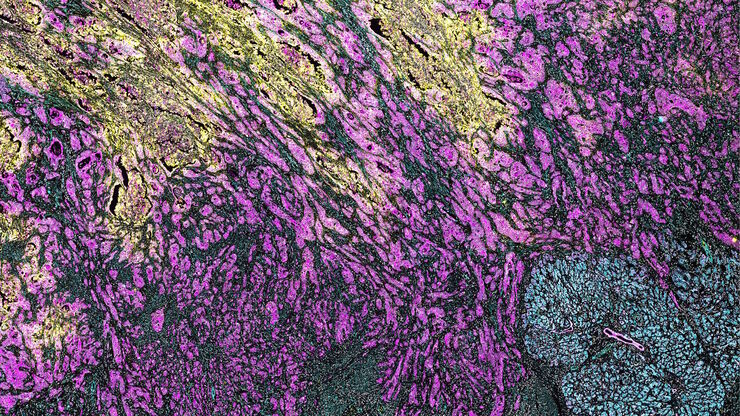
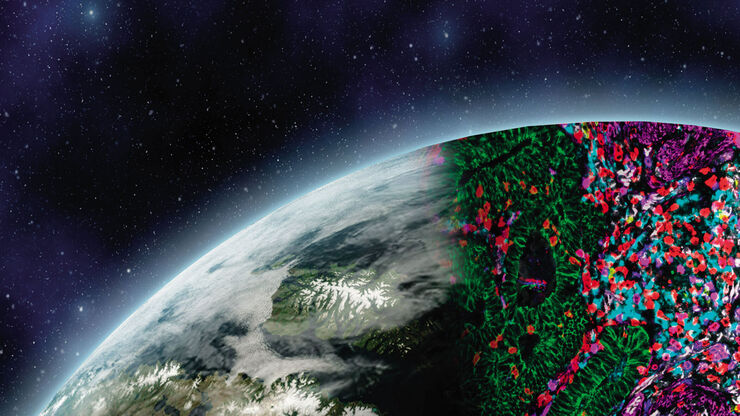
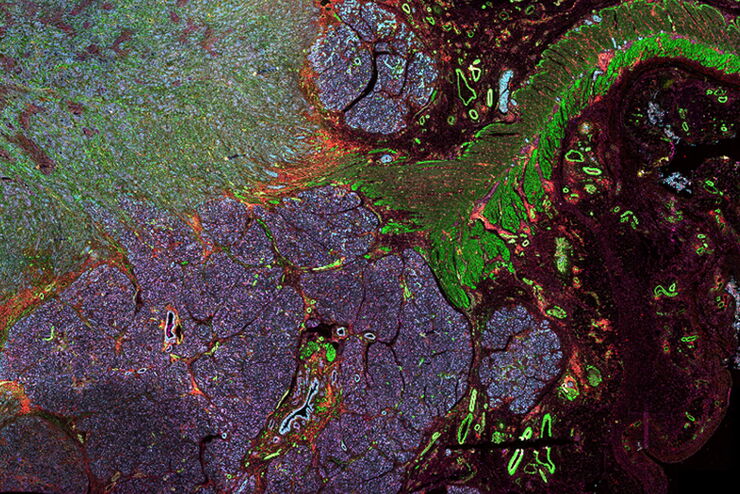
Cell DIVE
Microscópios óticos
Produtos
Página inicial
Leica Microsystems
Cell DIVE Solução de aquisição de imagens multiplexada
Transformando a pesquisa de tecidos com a multiplexação aberta.
Leia os nossos artigos mais recentes
Explore Alzheimer's Spatial Proteome with Big Data
Alzheimer's disease, a genetic and sporadic neurodegenerative condition, leads to cognitive decline in mid to late life, marked by β-amyloid plaques and tau tangles. With limited treatment options,…
Pesquisa de câncer
O câncer é uma doença complexa e heterogênea causada por células com deficiência na regulação do crescimento. Mudanças genéticas e epigenéticas em uma ou em um grupo de células prejudicam o…
Uncover the Hidden Complexity of Colon Cancer with Big Data
Colorectal cancer poses a significant health burden. While surgery is effective initially, some patients develop recurrent secondary disease with poor prognosis, necessitating advanced therapies like…
Dive into Pancreatic Cancer Research with Big Data
Pancreatic cancer, with a mortality rate near 40%, is challenging to treat due to its proximity to major organs. This story explores the complex biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC),…
Mapping Tumor Immune Landscape with AI-Powered Spatial Proteomics
Spatial mapping of untreated tumors provides an overview of the tumor immune architecture, useful for understanding therapeutic responses. Immunocompetent murine models are essential for identifying…
Spatial Analysis of Neuroimmune Interactions in Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by neurofibrillary tangles, β-amyloid plaques, and neuroinflammation. These dysfunctions trigger or are exacerbated by…
A Guide to Spatial Biology
What is spatial biology, and how can researchers leverage its tools to meet the growing demands of biological questions in the post-omics era? This article provides a brief overview of spatial biology…
Probing Human Alzheimer's Cortical Section using Spatial Multiplexing
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease and is characterized by the progressive decline of cognitive function. Spatial profiling of AD brain may reveal cellular…
Empowering Spatial Biology with Open Multiplexing and Cell DIVE
Spatial biology and multiplexed imaging workflows have become important in immuno-oncology research. Many researchers struggle with study efficiency, even with effective tools and protocols. Here, we…
AI-Powered Multiplexed Image Analysis to Explore Colon Adenocarcinoma
In this application note, we demonstrate a spatial biology workflow via an AI-powered multiplexed image analysis-based exploration of the tumor immune microenvironment in colon adenocarcinoma.
A Meta-cancer Analysis of the Tumor Spatial Microenvironment
Learn how clustering analysis of Cell DIVE datasets in Aivia can be used to understand tissue-specific and pan-cancer mechanisms of cancer progression
Mapping the Landscape of Colorectal Adenocarcinoma with Imaging and AI
Discover deep insights in colon adenocarcinoma and other immuno-oncology realms through the potent combination of multiplexed imaging of Cell DIVE and Aivia AI-based image analysis
Spatial Architecture of Tumor and Immune Cells in Tumor Tissues
Dig deep into the spatial biology of cancer progression and mouse immune-oncology in this poster, and learn how tumor metabolism can effect immune cell function.
IBEX, Cell DIVE, and RNA-Seq: A Multi-omics Approach to Follicular Lymphoma
In a recent study by Radtke et al., a multi-omics spatial biology approach helps shed light on early relapsing lymphoma patients
Accelerating Discovery for Multiplexed Imaging of Diverse Tissues
Explore IBEX: Open-source multiplexed imaging. Join the collaborative IBEX Imaging Community for optimized tissue processing, antibody selection, and human atlas construction.
Transforming Multiplexed 2D Data into Spatial Insights Guided by AI
Aivia 13 handles large 2D images and enables researchers to obtain deep insights into microenvironment surrounding their phenotypes with millions of detected objects and automatic clustering up to 30…
Understanding Tumor Heterogeneity with Protein Marker Imaging
Explore tumor heterogeneity and immune cell dynamics. See how quantitative imaging analysis reveals spatial relationships and molecular insights crucial for advancing cancer research and therapeutics.
The Shape of the Brain: Spatial Biology of Alzheimer’s Disease
Uncover cell identity and brain structure in Alzheimer's disease with Cell DIVE multiplexed imaging, demonstrating how spatial biology can lead to advances in therapy development for…
In Situ Identification of Cancer Stem Cell Niches in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Discover how multiplexed imaging technology uncovers cancer stem cell niches in Hepatocellular Carcinoma using multiplex immunodetection, revealing extracellular matrix dynamics. Explore precise…
Discover how Multiplexed Bioimaging can Advance Cancer Research
Explore multiplexing with up to 60 biomarkers, enabling advanced tumor imaging approaches to gather precise, spatially-resolved single-cell data that helps enhance cancer research and clinical…
Multiplexing with Luke Gammon: Advance your Spatial Biology Research
Learn how multiplexing imaging and spatial biology can help researchers better understand complex biological systems. In this interview, Dr. Gammon and Dr. Pointu of Leica Microsystems discuss pain…
Spatial Biology: Learning the Landscape
Spatial Biology: Understanding the organization and interaction of molecules, cells, and tissues in their native spatial context
Methods to Improve Reproducibility in Spatial Biology Research
Establish reproducibility results for a Cell DIVE multiplexed imaging study in cancer research using the BAB 200 automated system from ASLS and validated antibodies from CST
Characterizing tumor environment to reveal insights and spatial resolution
Antibodies from Cell Signaling Technology are validated for use with the Cell DIVE multiplexing workflow and used to probe cell lineages in the tumor microenvironment
Dig Deeper Into the Complexities of Pancreatic Cancer with Multiplex Imaging
Cell DIVE is an iterative staining workflow for multiplexed imaging that unveils biological pathways to dig deeper into the complexities of pancreatic cancer.
How is Microscopy Used in Spatial Biology? A Microscopy Guide
Different spatial biology methods in microscopy, such as multiplex imaging, are helping to better understand tissue landscapes. Learn more in this microscopy guide.
Complex Made Simple: Antibodies in Multiplexed Imaging
Build panels, plan studies, and get the most from precious reagents using this antibody multiplexing guide from Leica Microsystems
Multiplexed Imaging Types, Benefits and Applications
Multiplexed imaging is an emerging and exciting way to extract information from human tissue samples by visualizing many more biomarkers than traditional microscopy. By observing many biomarkers…
Hyperplex Cancer Tissue Analysis at Single Cell Level with Cell DIVE
The ability to study how lymphoma cell heterogeneity is influenced by the cells’ response to their microenvironment, especially at the mutational, transcriptomic, and protein levels. Protein…
Designing your Research Study with Multiplexed IF Imaging
Multiplexed tissue analysis is a powerful technique that allows comparisons of cell-type locations and cell-type interactions within a single fixed tissue sample. It is common for researchers to ask…
Be Confident in your Results with Cell DIVE Validated Antibodies
The Cell DIVE System includes a carefully curated list of hundreds of commercially available antibodies validated to offer optimal specificity and sensitivity in multiplexed imaging. That validation…